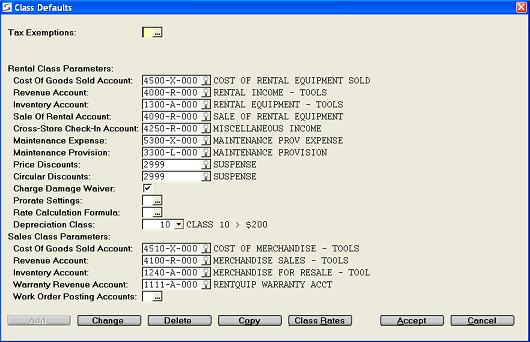
The following default parameters are used during the set-up of Rental Product Classes and Sales Product Classes.
An operator must be assigned a Security Role that allows permission to the Accounting - Product Class Defaults in order to access this Product Class Defaults utility.

The prompts to setup the class default values are:
In Canada, Tax 1 is generally GST or HST. In the United States, Tax 1 is State Sales Tax SST.
In Canada, Tax 2 is generally PST. In the United States, Tax 2 is generally County, Municipal or Local tax.
Enhanced Taxing
The purpose of the Enhanced Tax method is to allow more than two
tax codes to be tracked according to Location, and to be charged on
products, services, and Damage Waivers, and to allow for tax
exemptions on any or all of these charges.
The Enhanced taxing method can be activated in the Company Taxing Parameters.
An hourly rate to be expensed for maintenance can be entered in
the Maintenance Provision field for each rate code, in the expanded
rate structure detail of Rental Inventory
and in Groups.
If NO maintenance provision postings are required for a rate code,
the field can be left blank.
When invoices for this equipment at this rate are posted in the Daily Close, a Debit is then posted to the Maintenance Expense account and a Credit is posted to the Maintenance Provision Liability account as setup in Rental Product Classes.
Enter the default G/L Expense account to track discounts given through rate/price over-rides and discount percents given for products on the document.
Enter the default G/L Expense account to track discounts given through Circular pricing as setup in Circular Pricing.
Hours rented is always determined by hours billed on each contract, but for scheduling maintenance by the number of days rented, the conversion from Hours to Days can be based on 12 or 24 hours of actual usage.
This parameter controls the maintenance schedule default that
can be changed in document entry in Contracts, Reservations,
Quotes, and Worksheets.
Select one of:
The Maintenance Rental Period can be captured for each
non-bulk product detail on each contract to calculate when the
product is due for Type 1 maintenance as defined in the Maintenance Schedule.
If there is no 12/24 value reported for the contract, the value in
the Rental Product Class is used.
Note: Prorating does not apply to equipment out for less
than one day.
It applies to time out past a day, and also partial days past the
weekly or past the monthly period.
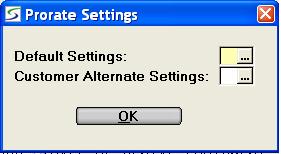
Window to set the prorate formula and select one of Default Settings or the Customer Alternate Settings as follows:
H (HALF-DAY) if equipment in this product class should have the
rental rates for partial days after one day, always prorated by the
half day.
The hours equal to a half day are determined by the value entered
for the next prompt O/T Hours In A Day.
N (NO) if this product class should NOT have the rental rates for partial days after one day, prorated.
F (FULL-DAY) if rental products in this product class should NOT
have the rental rates for partial days prorated but instead should
charge the full daily rate for each partial calendar day.
This processing uses the straight calendar date regardless of the
time of the day that the product goes out or is returned.
Note: Any Off Rental time must be greater than the hours in a calendar day, in order to effect a reduction in the billing of equipment in a class flagged to bill Full Days.
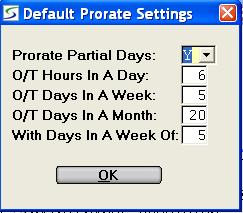
When Prorate Partial Days = Y (YES):
Enter the number of overtime hours equal to a day. This applies
after the first day.
The American Rental Association (ARA) suggests that the overtime
number of hours per day should be six. By accepting 6, the customer
will be charged 1/6 of the daily rate for each overtime hour. After
six hours, the customer is charged the daily rate.
Example: An Air Compressor at $60 a day, is rented for 2 days and 3
hours.
The rental charge would be calculated as follows:
(2 Days x $60) + (1/6 x $60 x 3 hours)
=120+30
=150
When Prorate Partial Days = H (HALF-DAY):
Enter the number of hours equal to half a day, after one day.
If the extra hours to be prorated are less than this, then half the
daily rate is charged.
If the extra hours to be prorated exceed this, then another full
day's rental is charged.
When Prorate Partial Days = N (NO):
This prompt will be ignored by the rate calculation as partial days
are not prorated for this class.
When Prorate Partial Days = F (FULL-DAY):
This prompt will be ignored by the rate calculation as partial days
are not prorated for this class.
The American Rental Association (ARA) suggests that the overtime number of days per week should be five. By accepting 5, the customer will be charged 1/5 of the weekly rate for each overtime day. After five days, the customer is charged for the full week.
Example: An Air Compressor at $240 a week, is rented for a week
for 1 week and 2 days.
The charge totals:
(1 Week x $240) + (2 Days @ 1/5 of $240)
= 240 + (2/5 x 240)
= 240 + 96
= 336
NOTE: If your firm charges the daily rate for each overtime day,
divide the weekly rate by the daily rate to determine the number of
Overtime Days In a Week to use.The American Rental Association (ARA) suggests that the overtime number of days per month should be 20. By accepting 20, the customer will be charged 1/20 of the monthly rate for each overtime day. After twenty days, the customer is charged for the full month.
Example: An Air Compressor rents at $720 for 4 Weeks, and is out
for 6 weeks.
The rental charges would be calculated as:
(4 Weeks @ $720) + (14 Days @ 1/20 of $720)
= 720 + (14 Days x $36)
= 720 + 504
= 1224
The American Rental Association (ARA) suggests that the number
of overtime days in a week after the first month should be 5.
At 5 days, the weekly rate will be charged.
Generally this prompt is set the same as O/T Days In A
Week.
Customer Alternate Prorate Settings
An Alternate
prorating formula can be setup company wide to apply to preferred
customers as designated in Customer
Information and preferred job sites designated in Customer Site Information, giving them even better
rental rates.
Window to set the alternate prorate formula. For a complete
explanation on how each field is used in the rate calculation refer
to the prorate Default Settings above.
Typical rate formula example:
HOURLY RATE IS .1667 TIMES THE DAILY RATE
4 HR MIN RATE IS .6667 TIMES THE DAILY RATE
OVERNIGHT RATE IS .6667 TIMES THE DAILY RATE
WEEKEND RATE IS 1.5000 TIMES THE DAILY RATE
WEEKLY RATE 4.0000 TIMES THE DAILY RATE
MONTHLY RATE 3.0000 TIMES THE WEEKLY RATE
This code also is used by the Auto Close From Fast Track Labor process when activated in the Company Estimate and W.O. Parameters to determine which rental classes should respect this feature.
Internal maintenance repairs on equipment included in Sales Inventory / Rental
Inventory, and standard Work Orders, post parts used values to
the standard Cost Of Goods Sold and Revenue Account
defined above.
A window is provided to enter default posting accounts for parts
used on equipment service Work Orders relating to the customer, as
follows:
Note: These accounts default from the standard COGS Account and Revenue Account, unless modified.
ACTIONS:
Additional actions provided by buttons on
the Product Class Defaults screen include:
View Default Product Class Rate Structure:
The Product Class defaults rates can also be viewed and printed by
clicking on the CLASS RATES button, as outlined in
Product Class Defaults Rates.
| Converted from CHM to HTML with chm2web Pro 2.85 (unicode) |